반응형
tkinter의 place() 함수는 위젯을 절대 좌표(픽셀 단위) 또는 비율(상대 좌표) 로 배치할 때 사용합니다.
즉, 화면에서 정확한 위치에 위젯을 두고 싶을 때 유용합니다.
📝 place() 함수의 주요 옵션
- x, y : 위젯의 왼쪽 위 모서리를 기준으로 하는 좌표 (픽셀 단위)
- relx, rely : 부모 위젯(창)의 가로, 세로 크기에 대한 상대 좌표 (0.0 ~ 1.0)
- width, height : 위젯의 가로, 세로 크기 (픽셀 단위)
- relwidth, relheight : 부모 위젯 크기에 대한 상대 크기 (0.0 ~ 1.0)
- anchor : 기준점을 바꿀 수 있음 (예: "center", "n", "e", "w", "s", "ne", "sw" 등)
📌 예제 1: 절대 좌표로 배치
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("place() 예제 - 절대 좌표")
root.geometry("300x200")
# 라벨
label1 = tk.Label(root, text="좌표 (50, 30)")
label1.place(x=50, y=30)
# 버튼
button1 = tk.Button(root, text="버튼 (150, 100)")
button1.place(x=150, y=100)
root.mainloop()
👉 픽셀 좌표 (50, 30)과 (150, 100)에 정확히 배치됩니다.
📌 예제 2: 비율(상대 좌표)로 배치
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("place() 예제 - 상대 좌표")
root.geometry("400x300")
label = tk.Label(root, text="가운데", bg="lightblue")
label.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.5, anchor="center") # 창의 가운데
button = tk.Button(root, text="오른쪽 아래", bg="pink")
button.place(relx=1.0, rely=1.0, anchor="se") # 오른쪽 아래 모서리
root.mainloop()
👉 창 크기가 변해도 위젯이 상대적인 위치를 유지합니다.
📌 예제 3: 크기와 위치 모두 비율로 지정
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("place() 예제 - 상대 크기")
root.geometry("400x300")
frame = tk.Frame(root, bg="lightgreen")
frame.place(relx=0.1, rely=0.1, relwidth=0.8, relheight=0.5)
label = tk.Label(frame, text="이 Frame은 창 크기에 따라 비율이 변함", bg="yellow")
label.place(relx=0.5, rely=0.5, anchor="center")
root.mainloop()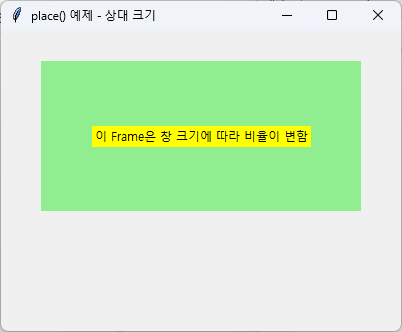
👉 창 크기를 늘리거나 줄이면, Frame과 Label이 자동으로 크기를 조절합니다.
✅ 정리:
- 정확한 위치 지정 → x, y
- 창 크기에 따라 자동 조절 → relx, rely, relwidth, relheight
- 기준점 변경 → anchor
원하시면 grid(), pack()과 비교해서 언제 place()를 쓰는 게 좋은지도 정리해드릴까요?
반응형
'Python > 파이썬 기초 강의(2024)★' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 음수, 2의 보수 구하기 파이썬 코드 (0) | 2025.09.10 |
|---|---|
| 파이썬 tkinter: pack(), grid(), place() 위젯 배치 비교 요약 (6) | 2025.08.30 |
| 파이썬: tkinter, grid() 이용한 위젯 배치, rowspan columnspan 셀 병합 (합치기) (8) | 2025.08.27 |
| tkinter, pack()을 이용한 위젯 배치 (2) | 2025.08.26 |
| 파이썬, pip: 패키지 및 라이브러리를 설치하고 관리하기 (2) | 2024.12.18 |